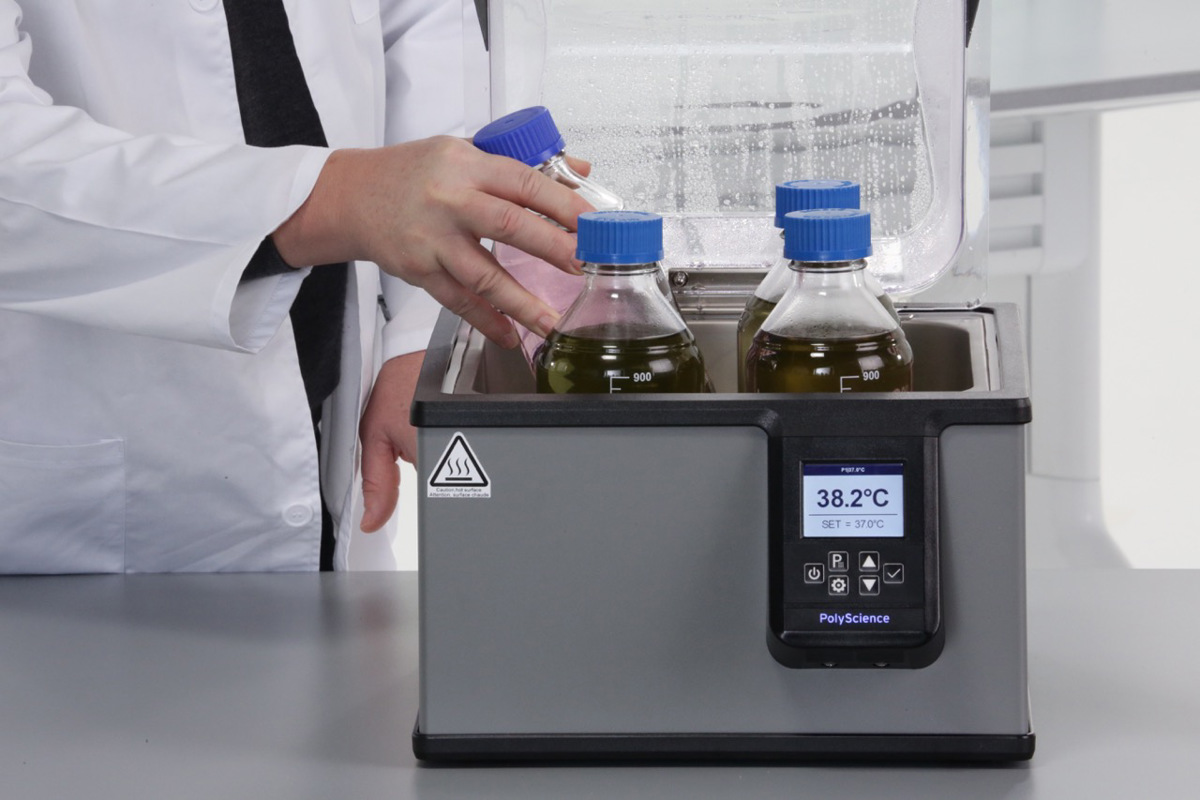
PolyScience produces a broad range of liquid temperature control equipment. In most cases, our products are not designed for a specific application but rather are engineered to provide stable heating or cooling over common operating temperature ranges. If your application requires maintaining a temperature near or below ambient temperature, then a refrigerated product such as a Recirculating Chiller or Circulating Bath is appropriate. The choice will depend on several factors. The following guidelines will help you determine the type of product, and model, best suited to your application:
- Fluid operating temperature range and set-point
- Cooling capacity (heat removal if set-point is near/below ambient)
- Ambient temperature (affects cooling capacity)
- Temperature stability (we offer choices from ±0.005°C to ±0.1°C)
- External application (open or closed-loop determines pump type)
- Reservoir size (if a bath is required)
- Pump pressure and/or flow rate (if pumping to an external application)
- External probe/programmability
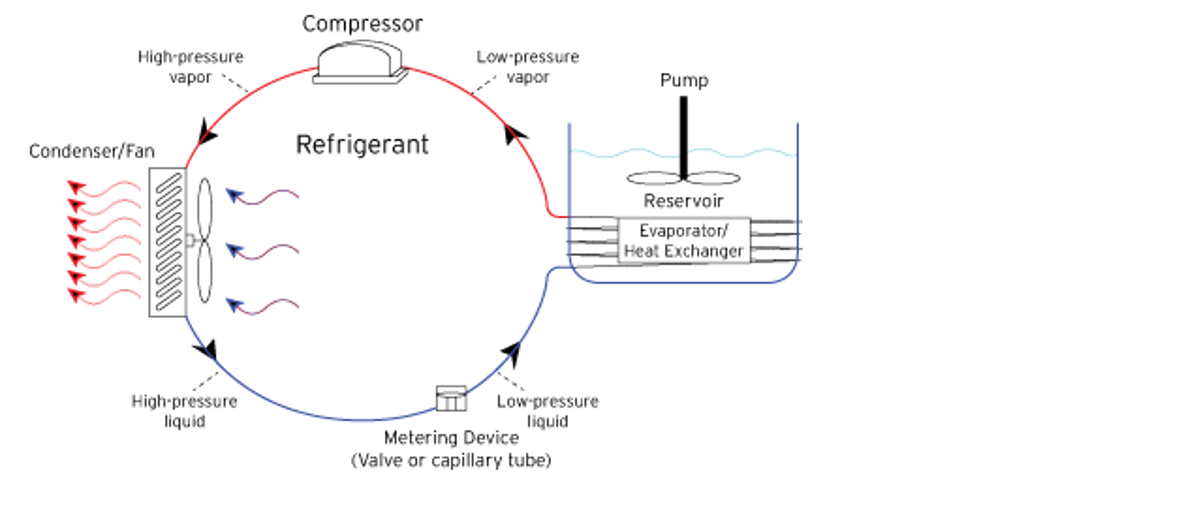
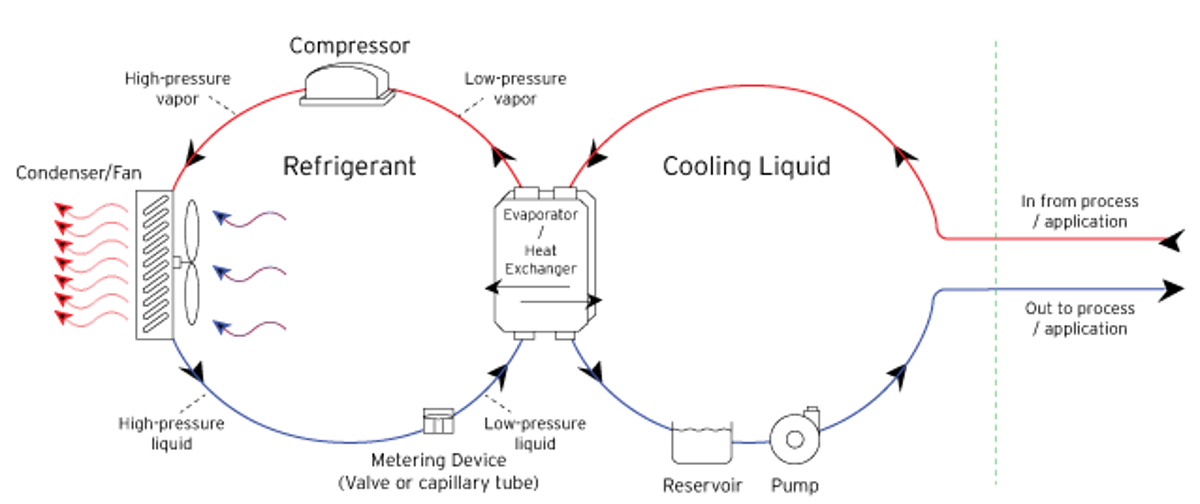
Because air-cooled, refrigerated products rely on ambient air to remove heat from the refrigeration system, the ambient air temperature will affect a unit's cooling capacity. As a general practice when selecting a refrigerated product, decrease the product's cooling capacity rating 1.3% for every 1° that the ambient air temperature exceeds 20°C. For example, if the ambient temperature where the Circulator or Chiller is located is 22°C, then the cooling capacity of the product will be reduced by 2.6%. At set-points near ambient, heating products that lack refrigeration will have difficulty maintaining temperature and stability.
A typical Circulating Bath uses the ambient air to remove heat from the refrigeration system which, in turn, removes heat from the process fluid.
A typical air-cooled Chiller uses the ambient air to remove heat from the refrigeration system which, in turn, removes heat from the process fluid.